Wheels for Inline Skates - A Complete Guide

- Wheel size: Influences speed and handling.
- Durometer: Indicates wheel hardness - impacts speed and how well vibrations are absorbed.
- Rebound: The speed with which the wheel returns to its original shape after being compressed.
- Grip: Reflects how effectively the wheel grips the skating surface.
- Wheel profile: Affects both speed and steadiness.
Overview
Overview
Which Inline Skate Wheels are Right for You?

Choosing the appropriate inline skate wheels becomes simpler if you know which type suits your skating style.
Irrespective of your inline skating preferences, considering the size and hardness of the wheels is essential. Match them accordingly with the surfaces you'll be gliding over.
| Type of Inline Skating | Features | Size Range / Hardness Range |
| Fitness Skate Wheels |
Smooth rolling Power transfer
|
80-110 mm 80A-88A |
| Freeskate Wheels |
Fast and responsive |
75-110 mm 84A-88A |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels |
Stable; shock-absorbing Smaller in size Either flat or round profiles |
55-80 mm 88A-95A |
| Roller Hockey Wheels |
Grippy and agile Excel in acceleration Some tailored for indoor use |
65-84 mm 72-84A
|
| Speed Skate Wheels |
Optimised for top speed Indoor/outdoor versatility |
100 mm-125 mm 83A-90A |
Inline Skate Wheels: Understanding Compatibility

Inline skate wheels are typically 24 mm in width, facilitating easy compatibility with your skate setup. Ensure the wheel's diameter does not exceed your rollerblade frame’s maximum specification for optimal fit.
Grasping concepts like hardness, rebound, grip, and profile ensures you pick wheels that not only fit but elevate the skating experience.
Proceed for further insight or check out our available options right now:
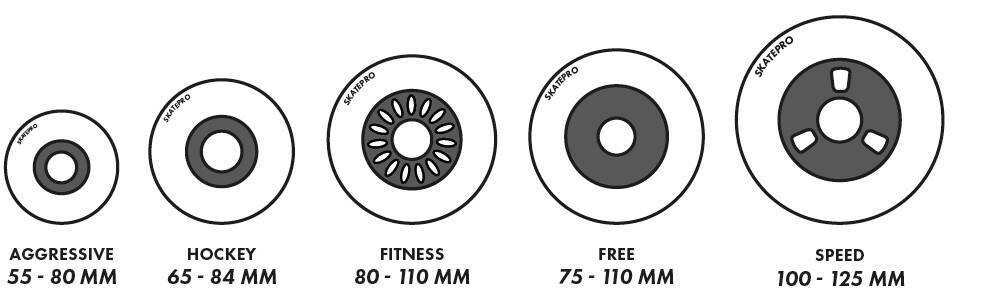
Inline Skate Wheel Size - Diameter Information
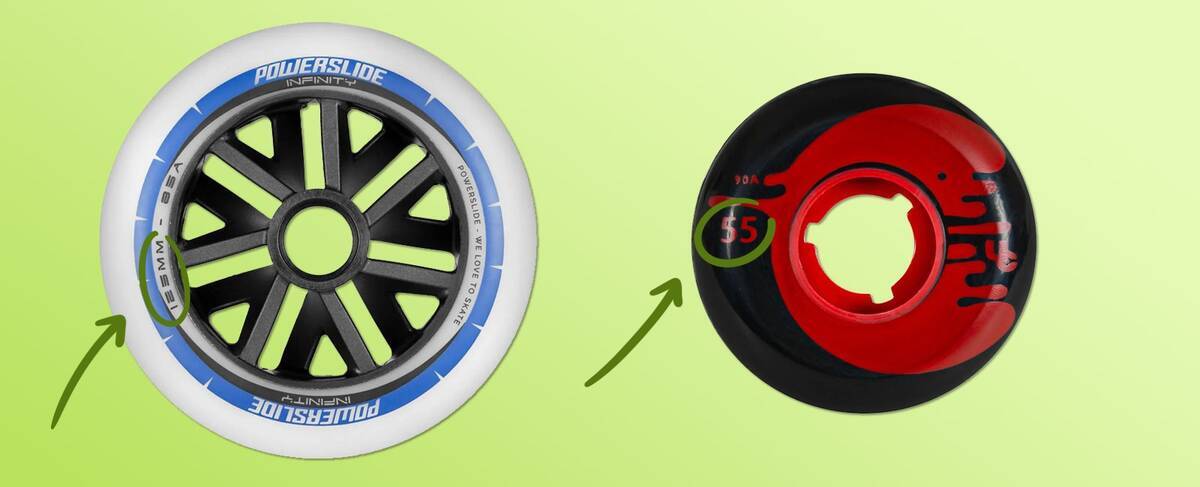

The wheel diameter for inline skates is measured in millimetres (mm) and is usually marked on the wheel's side. If absent, you can measure it manually.
Wheel size majorly influences various dynamics such as acceleration, speed, agility, and directional control.
Here's how diameter changes affect your skating performance:
- Smaller diameter: Improves acceleration and control.
- Larger diameter: Increases top speed and directional control.
We propose different diameter sizes for various skating disciplines, as depicted in this chart:
Size Recommendations for Inline Skate Wheels
| Skating Style | Size Range |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels | 55-80 mm |
| Roller Hockey Wheels | 65-84 mm |
| Fitness Skate Wheels | 80-110 mm |
| Freeskate Wheels | 75-110 mm |
| Speed Skate Wheels | 100-125 mm |
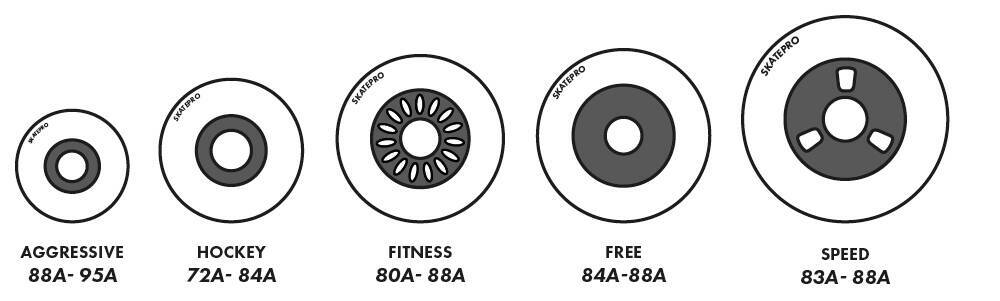
Hardness Levels for Inline Skate Wheels
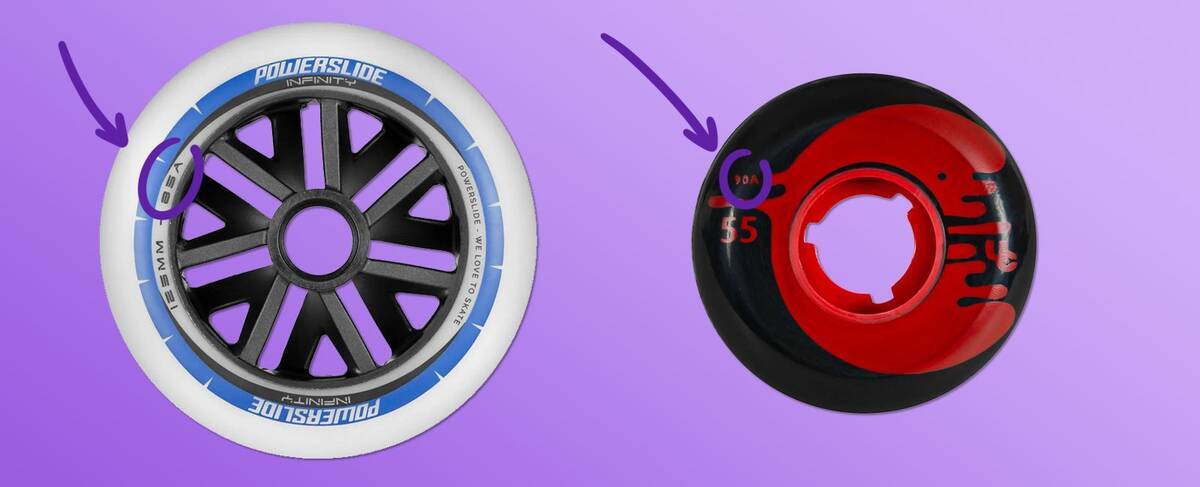

The hardness of wheels is measured using the durometer scale, commonly utilising the A-scale for inline skates. The scale displays a number followed by an A (like 82A), with higher numbers signalling harder wheels.
The A-scale facilitates quick identification of wheel hardness, and this rating is often printed on the wheel's side.
Choosing an appropriate hardness depends on your skating style. The chart below provides general guidelines:
Hardness Guidelines for Inline Skate Wheels
| Type of Skating | Hardness Range |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels | 88A-95A |
| Roller Hockey Wheels | 72A-84A |
| Fitness Skate Wheels | 80A-88A |
| Freeskate Wheels | 84A-88A |
| Speed Skate Wheels | 83A-90A |
Wheel hardness considerably affects performance across different surfaces and under varying conditions. Always be mindful of a wheel's hardness before purchasing, as it plays a substantial role in the performance of your skates.
Choosing Between Hard and Soft Wheels
Understanding the impact of wheel hardness on performance is essential, especially when comparing options with different hardness levels.
Here's how wheel hardness affects rollerblade performance:
Advantages of harder wheels- Enhanced speed
- Greater durability
- Reduced grip
- Poor vibration absorption
- Better grip
- Superior shock absorption
- Decreased speed
- Lesser durability
Typically, softer wheels excel in absorbing vibrations while providing good grip. On the contrary, harder wheels offer less vibration absorption and limited grip capabilities.
Alternative Hardness Measures
Some brands employ the footprint scale for determining wheel hardness. Below is a comparison to the A-scale:
- F0 - approximately 88A
- F1 - approximately 85A
- F2 - approximately 84A
- F3 - approximately 83A
Exploring the Rebound of Inline Skate Wheels
The rebound of a wheel signifies its ability to restore its original shape swiftly after deformation. High rebound enhances speed by returning to shape quickly, while low rebound dissipates energy, reducing speed. Thus, wheel rebound significantly affects your skating speed.
Quality wheels boast a high rebound, often labelled as SHR urethane, or Super High Rebound. While there is no standard way to compare rebound, economical options usually offer less rebound, while premium brands ensure superior rebound.
Understanding Inline Skate Wheel Grip
The grip of inline skate wheels is influenced by the polyurethane (PU) formulation in the rubber, with hardness being a critical factor.
The relationship between wheel hardness and grip is straightforward:
- Softer wheels: Offer more grip.
- Harder wheels: Provide less grip.
The rolling surface significantly influences grip. On smooth surfaces like rinks, more grip prevents slipping, whereas on coarser terrains like asphalt, grip is less critical.
Accordingly, harder wheels are suitable for rough surfaces, as grip concerns are minimal.
Profile Variations in Inline Skate Wheels
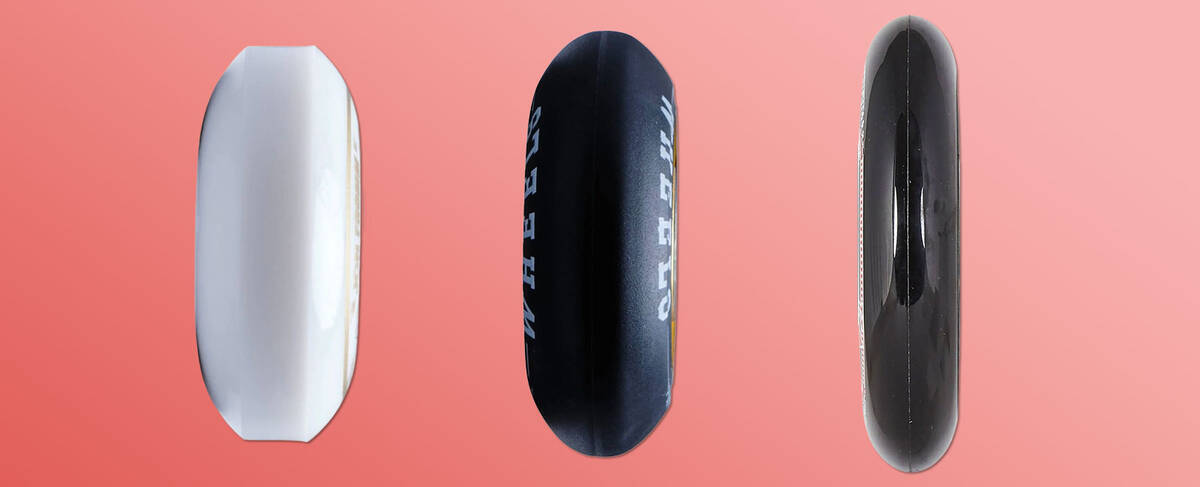

Inline skate wheel profiles range from flat to pointed. The profile defines how much of the wheel contacts the surface. A flat profile has a larger contact patch compared to a pointy one.
Pointy profiles are prevalent in various skating disciplines from fitness to high-speed setups, minimizing friction and resistance. They are favoured for their versatility and speed advantages.
Flat profiles cater to aggressive skating, prioritizing stability for trick landings over speed.
Rounded profiles are preferred for freeskating and aggressive skating. These are commonly used in flat setups and ease the risk of wheel bites. Rounded profiles are beginner-friendly due to their manageable control.
Cores of Inline Skate Wheels

The hub, or core, lies at the wheel's centre, housing the bearings. Hubs are usually crafted from hard plastic or aluminium. While aluminium cores may weigh more (depending on the design), they boast greater impact resistance and longevity over plastic ones.
Various hub types exist, including:
- Solid core: Very strong, but heavier.
- Spoked core: Lighter, sacrificing some durability.
- Hollow core: Balances between weight and strength.
For better performance, choose wheels that offer durability without excessive weight to enhance skating efficiency and reduce fatigue.
Caring for Inline Skate Wheels
Optimising the life of your wheels can lead to substantial savings, considering they wear out faster than most other components of your skates. Regular rotation ensures they wear evenly, maintaining optimal skate performance.
Wheels naturally wear down, creating a flat diagonal surface on their inward side. This wear pattern disrupts skating technique, and rotating the wheels when this happens can remedy it.
By rotating rollerblade wheels, one can maintain the uniform shape of the wheels. For anyone unsure of how to move forward with this, we recommend our wheel rotation guide:
If you’re uncertain about whether it’s time to replace your inline skate wheels, take a look at our helpful guide on the topic:
Need assistance with wheel installation? Here’s the answer:
For those seeking advice on the general upkeep of inline skates, our detailed online guide is an excellent resource:
... And What About the Bearings?
We offer dedicated guides specifically for wheel bearings. This particular guide covers all the essential information on their functionality:
If your roll isn't as smooth as it previously was, the bearings might be the reason. In such cases, it's worth considering a comprehensive cleaning and new lubrication: